Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Recent posts
Do you have any doubt?
My goal is to help them regain not only function, but also the quality of life they deserve. If you are experiencing pain, movement limitations or injuries to your hands, I am here to offer you my experience in the field. Together, we can chart a path to recovery and restoration of vitality to your hands.
Categories
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is an illness that affects 4-5% of the population between the ages of 40 and 60. It can occur in a 65-80% for women specifically and a 50-60% of the cases it affects both hands.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
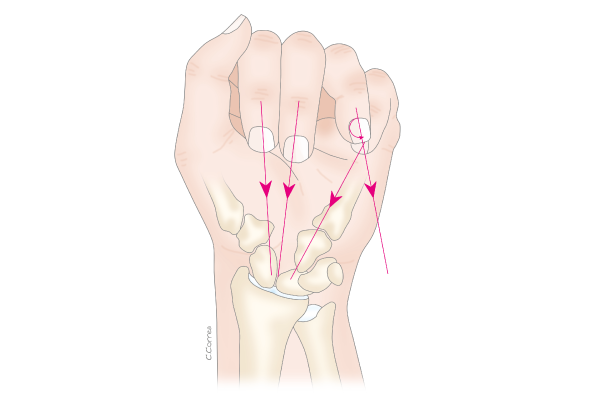
It’s an anatomical canal located on the palm of the hand, the floor is formed by the bones of the wrist and the roof is a strong ligament called the transverse carpal ligament. Within the tunnel there are 9 finger flexor tendons and the median nerve. The latter, is the most superficial of all the structures and is responsible for feeling in the thumb, index, middle and external half of the ring finger. The nerve is the most sensitive structure in the tunnel and it has a very low tolerance to pressure.


What are the symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
People describe the symptoms as cramps, tingling, pain, numbness and loss of strength, they are usually more intense in the evenings.
What causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Degenerative changes in the tendon end up causing them to increase in diameter thus making the symptoms appear. Another factor could be a fracture or an osteoarthritis of the wrist which reduce the diameter of the tunnel, additionally, the abnormal distribution of liquids that happens during pregnancy or hyperthyroidism can also cause carpal tunnel syndrome.

What are the main symptoms?
Burning sensation, tingling, heaviness, or electric pulses that are usually accompanied by pain that shoots towards the forearm, elbow or shoulder. All these symptoms could get worse in the evenings but can be improved by lifting or shaking the hands. Day-to-day activities can trigger these symptoms like, holding a newspaper or phone, and even driving. At an advanced stage of this illness a reduction of muscle mass will be noticed on the palm of the hand.
How is it diagnosed?
The diagnostic is based on:
- Symptoms described by the patient.
- Test results from examinations done by the specialist.
- Electromyography results and nerve conduction speed, this exam will determine the how compressed the nerve is (mild, moderate or severe) and depending on this the specialist will determine the best course of action.
What are the non-surgical options?
In the initial stages of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome it’s recommended to have a more conservative approach to treatment by using anti-inflammatories, braces or wrist guards for nocturnal use.
For patients that are expecting the non-surgical treatment should be followed for as much time as necessary, as symptoms usually disappear on their own after childbirth.
When should the surgical approach be considered?
Surgery should be considered an option when patients have symptoms all day, have muscular weakness, or when the illness doesn’t improve with the non-surgical treatment. Senior patients have a higher indication for surgical treatment than younger ones, this is due a slight atrophy of the thenar eminence, which means a slower recovery time for them. It has been proven that the more evolved the syndrome is, the slower recovery time will be.
What does the surgery entail?
The surgery will release the transverse carpal ligament.


Can both hands be surgically intervened at the same time?
It’s not recommended. Patients should be independent after a surgery so one hand should always be free to perform basic daily tasks (eating, dressing, cleaning). If both hands are intervened, the patient will have to rely on others to do these tasks.
Moreover, it’s been frequently noted that when patients with CTS on both wrists have one hand operated, the other hand will improve spontaneously without it needing surgical treatment.
The first hand to be operated on would be the most painful one or the one with the most symptoms.